Cartibeads™ are hyaline-like cartilage mini-grafts. Our patented method allows chondrocytes (cartilage cells) to first be expanded and then regain their capacity to secrete a hyaline matrix.
CARTILAGE DEFECT AND OSTEOARTHRITIS
Cartilage defect and osteoarthritis
Articular cartilage is a soft, white tissue that covers the ends of articulating bones and helps joints to move smoothly. It’s made of cells named chondrocytes embedded in a self-secreted hyaline matrix. This matrix’s composition has specific biomechanical properties to absorb shocks, particularly in load-bearing joints such as the knees.
Unfortunately, cartilage has very limited capacity for self-repair when damaged. Aging and repetitive trauma occurring during intensive sport practice are the major risk factors for cartilage degeneration. Cartilage injury can often evolve towards osteoarthritis (OA).
OA is the most common degenerative joint condition, and the knee is the most frequently affected joint. It causes pain, swelling and stiffness, affecting a person’s ability to move freely. OA affects over 300 million people worldwide, with prevalence increasing substantially with age.
Current management strategies for OA include physical therapy, pain medication, and surgical treatments, including joint replacement by prosthesis. However, this invasive surgery is not commonly proposed to patients under 60. Moreover, prostheses need to be replaced every 15-20 years, and do not completely relief pain for the majority of patients. Treatment of cartilage lesions is therefore key to minimize progression towards OA.
Current treatments
Several palliative treatments are available to reduce the symptoms of cartilage lesions, such as anti-inflammatory medications or injection of hyaluronic acid. However, these treatments do not to regenerate cartilage.
There are also surgical treatments aimed to restore and preserve joint function. Microfracture, for instance, consists in drilling the bone under damaged cartilage to release bone marrow cells. It is a common practice for small cartilage lesions (<2 cm2). Yet, microfracture results in a cartilage tissue of poor quality, called fibrocartilage, which is not a long-lasting treatment due to its inferior biomechanical properties. Osteochondral allografts offer an alternative approach for large lesions (>3 cm2) by harvesting plugs of cartilage and underlying bone from cadaveric donors. Allografts offer a high-quality source of healthy tissue, but their availability, viability, risk of disease transmission, and immune response (due to bone marrow presence) remain areas of ongoing development. Moreover, their lateral integration (cartilage-cartilage) remains challenging.
Allogeneic Cartibeads™ could overcome these limitations by providing a standardized, high-quality product suitable to treat large lesions. This innovative product is implanted in the lesions by intra-articular administration in the affected knee joint with a simple surgical procedure. The mini-grafts just need to be placed on the defect area, which they quickly fill on their own. Two clinical trials are currently ongoing to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of Autologous and Allogeneic Cartibeads™ in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions.
Cartibeads™
A novel tissue engineering solution
to repair cartilage defects

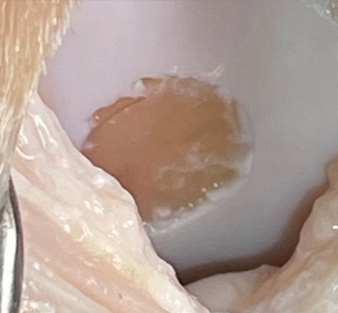
Cartibeads™ are intended for the treatment of cartilage lesions, which have a very limited capacity for self-repair.
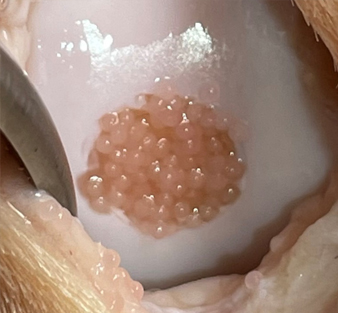
Upon implantation, Cartibeads™ fuse among each other and integrate with the surrounding tissue.
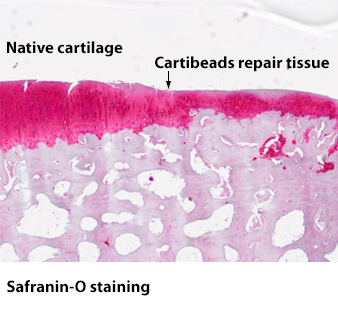
Preclinical data have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of Cartibeads™ in the treatment of cartilage lesions, showing that the Cartibeads repair tissue maintained hyaline quality at 6 months follow-up.